Gynecomastia in men
Gynecomastia in men
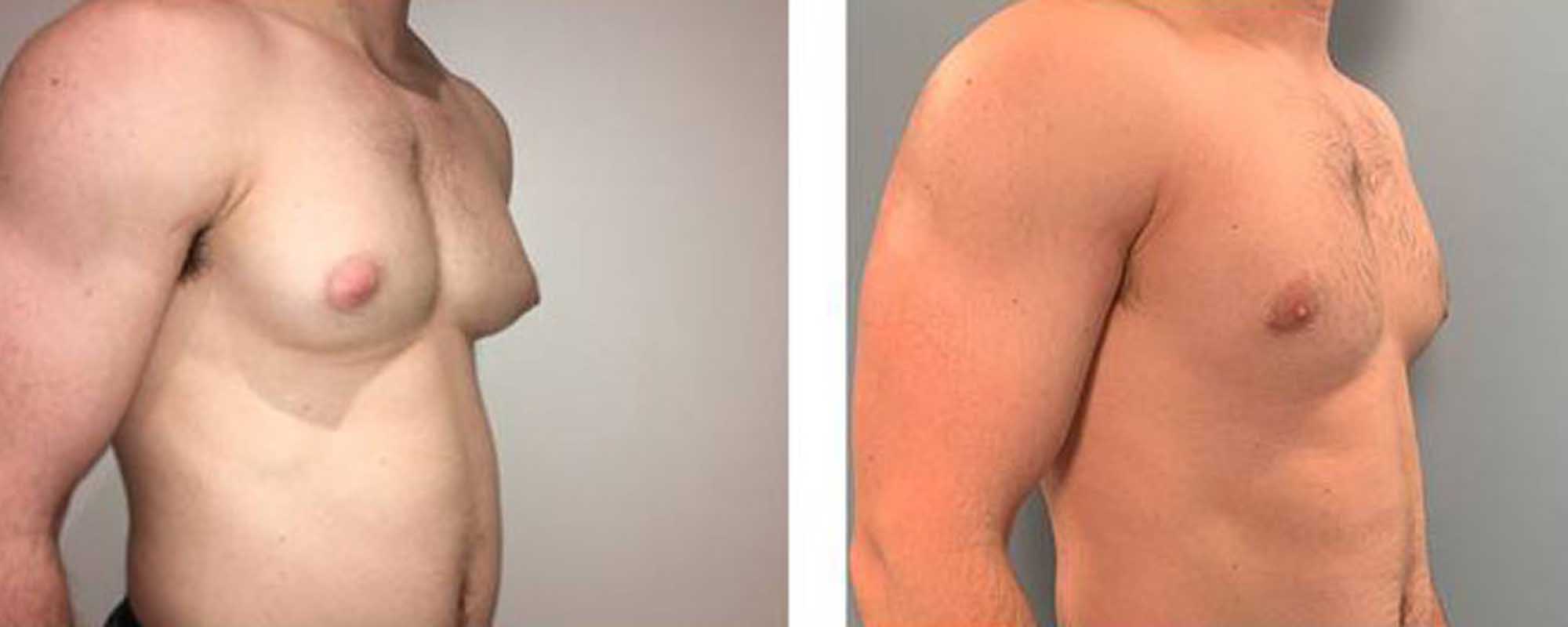
All boys are born with a little amount of breast tissue, despite the fact that men’s breasts do not develop in the same way that women’s do, and the disease known as gynecomastia, which causes the chest tissues of boys and men to enlarge, is caused by an imbalance between two hormones in the body.
Male bodies also generate oestrogen, which is the hormone that causes sexual development in girls. During puberty, testosterone, which is produced by the bodies of boys, stimulates the growth of their sexual organs. When a boy reaches puberty or when an adult man’s body begins to produce a small amount of the hormone thyrosterone, the balance of hormones in their bodies is upset. Occasionally, when this occurs, the amount of oestrogen in their bodies rises, causing their breast tissue to swell. About half of the boys are in adolescence. Two-thirds of adult men report having this ailment to some extent.
Why does gynecomastia occur?
Gynecomastia, or the growth of male breasts, is a condition that can be brought on by a variety of factors, including hormonal imbalances that result in puberty or aging-related changes to the body, as well as:
Conditions that affect the testes’ ability to produce testosteron
- Thyroid issues since this gland’s hormones are responsible for controlling growth and sexual development.
- Lung, adrenal, or pituitary tumours are a few examples of cancerous growths.
- Using medication to treat conditions such as heart disease, depression, ulcers, or using illicit narcotics.
- A liver condition.
- The possibility of increased oestrogen production due to obesity.
- Due to the mother’s hormones still being in their system, some newborns may have temporary gynecomastia.
Symptoms
The first indication of gynecomastia is the formation of a mass of fatty tissue under the nipple; occasionally, this area is uncomfortable or painful. The breasts may also enlarge unevenly, causing one to rise higher than the other.
Diagnosis
In the event that your doctor suspects you of having gynecomastia, he or she will likely examine you to rule out any skin conditions, solid lumps, or fluid-oozing lesions that could be an indication of breast cancer, which can, albeit infrequently, strike males.
He will request samples of your blood and urine to check for any issues that could be affecting your hormone levels. He or she might also perform a biopsy or mammography to check for cancer.
Treatment
- On their own, most instances tend to progressively improve.
- For issues involving hormones, your doctor could suggest seeing an endocrinologist.
- The type of treatment may vary depending on your age, general health, how long the disease persisted, and how your body reacts to specific treatments.
- Gynecomastia that manifests throughout adolescence typically goes away on its own, taking anywhere between six months and three years.
- You will need to address the underlying condition if it turns out that your hormone imbalance is caused by something else. The hormonal imbalance that promotes breast growth may be treated with medicine for the patient. The patient may occasionally have surgery to suction or remove extra fat from the breast.
Behavioral response
The doctor might suggest that you get treatment from a mental health professional for the psychological issues related to this disease since some studies suggest that gynecomastia can lead to eating disorders, anxiety, or depression in those who have it, particularly in young boys.
